
Understanding Chapter 14
Notifiable transactions for listed companies
CGj reviews the second session of the Institute’s Listing Rules Foundation Course Series, which focused on the notifiable transaction provisions under Chapter 14 of the Listing Rules.
Highlights
- Chapter 14 of the Main Board Listing Rules deals with notifiable transactions, outlining a number of specific classifications that require varying levels of disclosure and shareholder approval, based on the significance of the listed issuer in terms of size
- the current economic downturn is complicating transaction management, with lower revenues, profitability and market capitalisation causing more transactions to exceed regulatory thresholds, triggering additional disclosure and shareholder approval requirements
- operating across jurisdictions necessitates thorough risk management, clear internal training and consistent communication with regulators
General principles
Chapter 14 of the Main Board Listing Rules outlines the requirements for notifiable transactions, which are transactions that must be disclosed to, and/or approved by, a listed issuer’s shareholders based on their significance in terms of size. Notifiable transactions under Chapter 14 include, but are not limited to, transactions in relation to acquisitions and disposals of assets, transactions involving leases and options, provision of financial assistance and formation of joint ventures (see ‘Type of transactions and exemptions’). They are classified according to the percentage ratios that compute their size, as well as determine the level of disclosure and shareholders’ approval requirements.
Seminar speakers reminded listed issuers that, where a transaction falls within the categories of notifiable transactions set out in Chapter 14, it is subject to the Listing Rule requirements, even if that transaction is in the ordinary and usual course of business of the listed issuer.
In order to avoid any non-compliance, seminar speakers also advised companies to put in place robust risk management and internal control measures to ensure proper due diligence, clear internal communication and ongoing monitoring of transactions.
Calculation and classification of percentage ratios
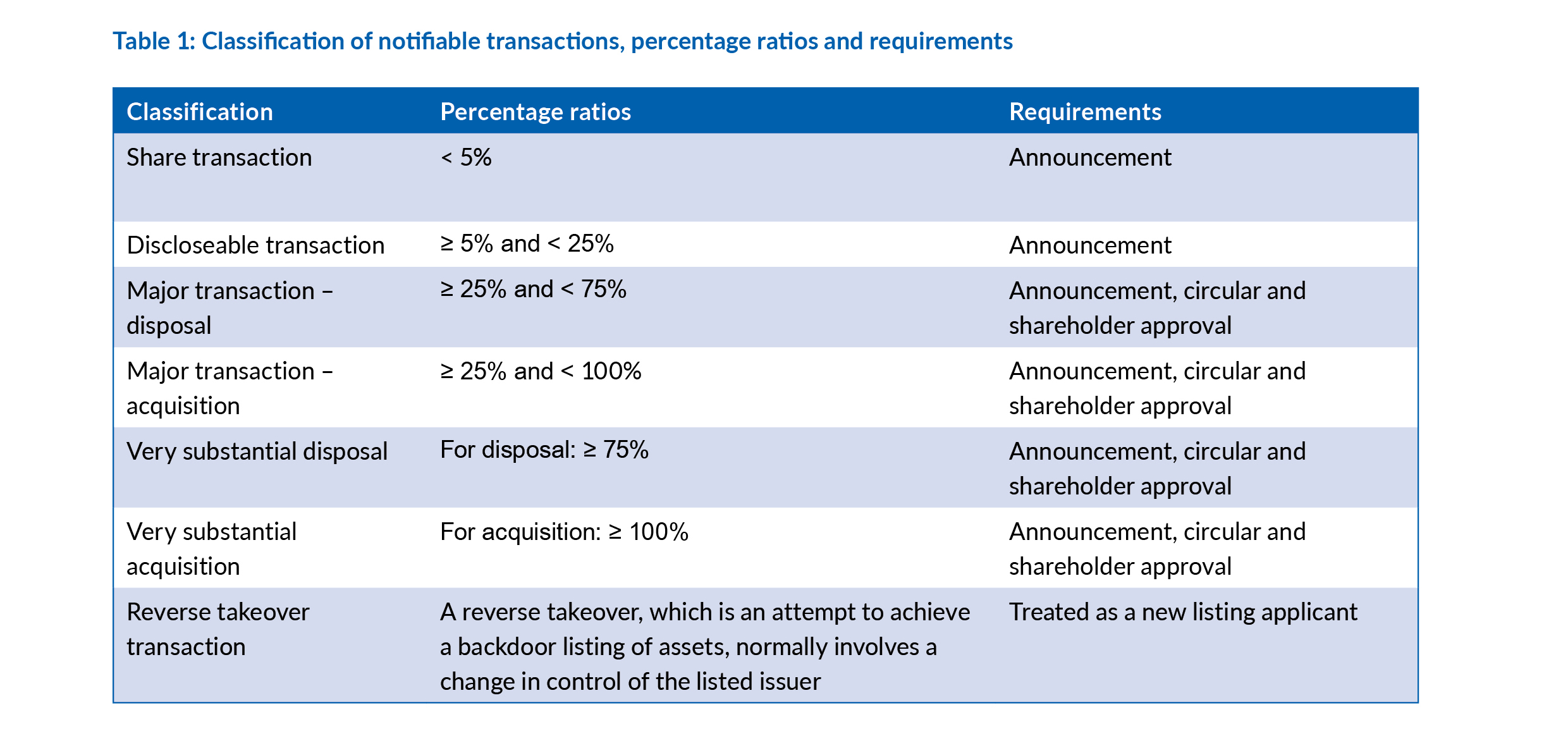
Under Chapter 14, a notifiable transaction may be classified by its nature and the applicable percentage ratios as a share transaction, a discloseable transaction, a major transaction, a very substantial disposal, a very substantial acquisition or a reverse takeover transaction (see Table 1). Depending on the specific classification, the transaction is subject to different compliance requirements, including announcement, circular and shareholders’ approval.
Seminar speakers shared details regarding the calculation of the percentage ratios, namely, the assets ratio, the profits ratio, the revenue ratio, the consideration ratio and the equity capital ratio.
Where any calculation of the percentage ratio produces an anomalous result or is inappropriate to the sphere of activity of the listed issuer, the listed issuer may seek prior consent of The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (the Exchange) to disregard the calculation and must provide alternative test(s) that it considers appropriate for consideration by the Exchange.
After calculating the relevant percentage ratios for a transaction or a series of transactions, a listed issuer can determine if that constitutes a notifiable transaction and can identify the appropriate classification.
Seminar speakers also pointed out that to prevent an issuer from splitting a large transaction into two or more smaller transactions to circumvent the notifiable transaction rules, the Exchange may require the issuer to aggregate a series of transactions if they are all completed within a 12-month period, and/or if they fall under the circumstances set out in the relevant Listing Rules.
Navigating financial control in a challenging economic climate
In the face of a turbulent financial environment, listed companies face numerous challenges related to financial control and compliance. During the panel discussion moderated by Michael Ling FCG HKFCG, Institute Technical Consultation Panel Chairman, and Joint Company Secretary, CLP Holdings Ltd, industry experts explored the key issues that companies must address.
Tommy Tam, Partner, Clifford Chance, highlighted challenges faced by listed companies. ‘Recently, low market valuations have led to a concern,’ Mr Tam noted. ‘Transactions are more likely to trigger a very substantial acquisition, which is more complex compared with a major transaction.’
“transactions are more likely to trigger a very substantial acquisition, which is more complex compared with a major transaction”
Tommy Tam
Partner, Clifford Chance
Polly Wong FCG HKFCG(PE), Institute Professional Development Committee member, and Company Secretary and Group Financial Controller, Dynamic Holdings Ltd, emphasised the challenges of operating across multiple jurisdictions, the regulatory requirements of which are different. She also noted the emergence of high-risk financial products in the market, such as those promising high yields, underscoring the importance of thorough risk assessment and internal training. ‘Effective risk management and educating internal staff on compliance rules is crucial,’ Ms Wong stressed.
Polly Wong FCG HKFCG(PE), Institute Professional Development Committee member, and Company Secretary and Group Financial Controller, Dynamic Holdings Ltd, emphasised the challenges of operating across multiple jurisdictions, the regulatory requirements of which are different. She also noted the emergence of high-risk financial products in the market, such as those promising high yields, underscoring the importance of thorough risk assessment and internal training. ‘Effective risk management and educating internal staff on compliance rules is crucial,’ Ms Wong stressed.
“effective risk management and educating internal staff on compliance rules is crucial”
Polly Wong FCG HKFCG(PE)
Institute Professional Development Committee member, and Company Secretary and Group Financial Controller, Dynamic Holdings Ltd
Panellists urged listed companies to be more vigilant in managing transactions, ensuring compliance
and maintaining transparent communication with regulatory bodies to navigate complex financial requirements more effectively.
Session 3 of the Institute’s Listing Rules Foundation Course Series was held in August this year. Look out for a review of that session in the next edition of CGj.
Type of transactions and exemptions
- Acquisitions and disposals. An issuer or its subsidiaries may acquire or dispose of assets, which include the acquisition and disposal of equity interest in a company, tangible and intangible assets, and financial
assets. - Deemed disposals. This refers to situations where a subsidiary’s issuance of new shares reduces the
parent issuer’s equity interest in that subsidiary. This equity reduction is treated as a deemed disposal by the issuer. - Formation of joint ventures. Formation of a joint venture involves an issuer partnering with third
parties to establish a new entity. However, subject to the relevant requirements of the Listing Rules, a joint venture is not considered a notifiable transaction if it involves a single-purpose project or a transaction of a revenue nature within the issuer’s ordinary business. - Financial assistance. Financial assistance refers to any action involving the granting of credit, lending money, offering indemnity against loan obligations, or providing guarantees or security for a loan. The Listing Rules set out certain exceptions to financial assistance provided by banks and securities firms in their ordinary course of business, as well as by listed issuers to their subsidiaries.
- Leases. Under Chapter 14, leases include finance leases and operating leases.
- Options. An option is treated as a transaction under Chapter 14 when an issuer grants, acquires, transfers or exercises an option. Additionally, if an issuer terminates an option, it is considered a transaction unless such termination follows the original agreement terms and does not involve any payment for penalties, damages or other compensation.


